NFT Smart Contract Development
We're going to create our own NFT smart contract using Remix. What we will end up doing is creating an NFT contract that is ERC 721 compliant. So most of the NFT collections out there are ERC721, so that is what we're going to build out today. We are going to write the solidity code and let's see if we can deploy that to a chain. Our NFTs will be mintable so any user can go and mint these NFTs. We will try to add some token URI as well so that our NFT is related to art.
So to create our code what we are going to do is we are going to use this awesome open source library called open zeppelin. They also provide us with a wizard to create your own ERC contracts. We will be able to see their ERC20 contract. We just provide the name and the symbol and that's it, your ERC20 coin is ready. They also provide us with ERC721 which is the NFT standard that we're going to work on today. They also provide ERC1155 which is a different NFT standard. We're going to use ERC 721 today. It is the standard that we're going to work. It is used in most of the famous NFT projects.
So what OpenZeppelin does is it gives us the bare minimum part and then we can customize the code as and when required for ourselves. Let's say we want to change the name of our token and symbol. We can also provide a base URI which is required if you want to associate some sort of art or metadata with your NFT. If you want to let's say create a PFP NFT where you know there are 10,000 images and whatnot. The base URI is always sort of required or expected. We can add other features as well for example auto-increment IDs. We can also make this NFT enumerable.
We’ll be using Remix and if you don't know what Remix is, it’s an awesome Ethereum Solidity IDE provided by the Ethereum foundation. it comes with all the things required for you to create a Solidity project and deploy it. In some sense, our NFT contract is done like this and it is a proper functioning contract that will go for whatever number that you want. But right now only the owner can come and mint a new NFT and they can do it 10, 000 times or more. Let's say you want to create an NFT smart contract where people come and mint their own NFT even though you are the one who is providing the art but people will come and mint NFT. To achieve that, we will refactor the safeMint method and make it so that all users are able to access it
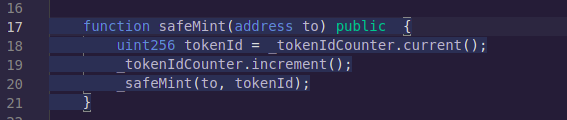
Let's just go ahead and first compile this NFT contract and see if there is any problem with it. There's no problem, now we'll go and deploy this on our small Ethereum chain that we get with Remix by clicking on deploy.
Now if we open and see our deployed contract we'll see that there are a bunch of methods that we can see right so we can use this to test our contract functionality like checking total supply, checking owner of NFT with ownerOf, etc. So let’s go ahead and mint one NFT for ourselves. We'll copy our own account address and then call the safe mint part by clicking on transact and as soon as we do that our NFT is minted and our total supply is incremented by 1.
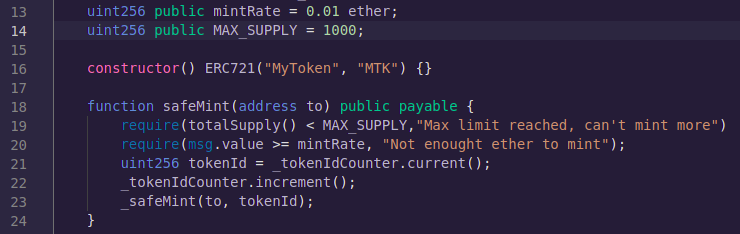
Since NFT minting should be accompanied by some amount but in our case, it is now a payable function. Hence to support payment we make our safeMint function payable and add a mintRate i.e. minting amount of our NFT (not including the gas). Then we add a check to see if the received amount is greater than or equal to our mintRate. If not we throw an error with some proper message,

We first compile it and check for any errors and then we go ahead and deploy our updated contract. With this, our safeMint method should be denoted with a red color and we can go ahead and test it to see if a minimum amount of ether is required or not to mint our NFTs. We can check the mintRate because it's a public method so it's visible. The mint rate that we see is one followed by so many zeros because it's in wei which is 1 by 10 to the power 18 ether
Now the problem with this is that the ether sent to this contract is not retrievable by the owner because you know we the owner whatever amount of ether we have collected we need to withdraw it so what we need to do is we have to create a function which is called to withdraw the funds. The function should be public and only ownable so only the owner who is the owner of this contract the person who has deployed this smart contract only they can withdraw ether. So now to figure out who is the owner of the smart contract we will use the ownable which returns the owner. Then we want this address to be payable because we want to send some ether to that address then we call transfer on that payable address and what we do is we call address (this) so this way we get the smart contacts address and then we write the balance so whatever the balance is we will just withdraw it. We can add a check to see that this balance is more than zero. We can go ahead and compile and deploy this contract to check if our withdrawal functionality works or not.

So this is how people basically make money by selling NFTs by letting you mint NFT on their own contract so if you were wondering how people do that is your answer. Now our minting contract is almost ready, right now it lets people mint whatever amount of NFTs that they want without having an upper ceiling. So what we’re going to do is to create a uint which will be public with the name MAX_SUPPLY which is 1000 (for our contract can be any number) and we are going to require another thing over at our safeMint method which will be that total supply should be less than max supply




 Languages
Languages ENGLISH
ENGLISH
 Work
Experience /
Trainings / Internship
Work
Experience /
Trainings / Internship
 Education
Education

